Context:
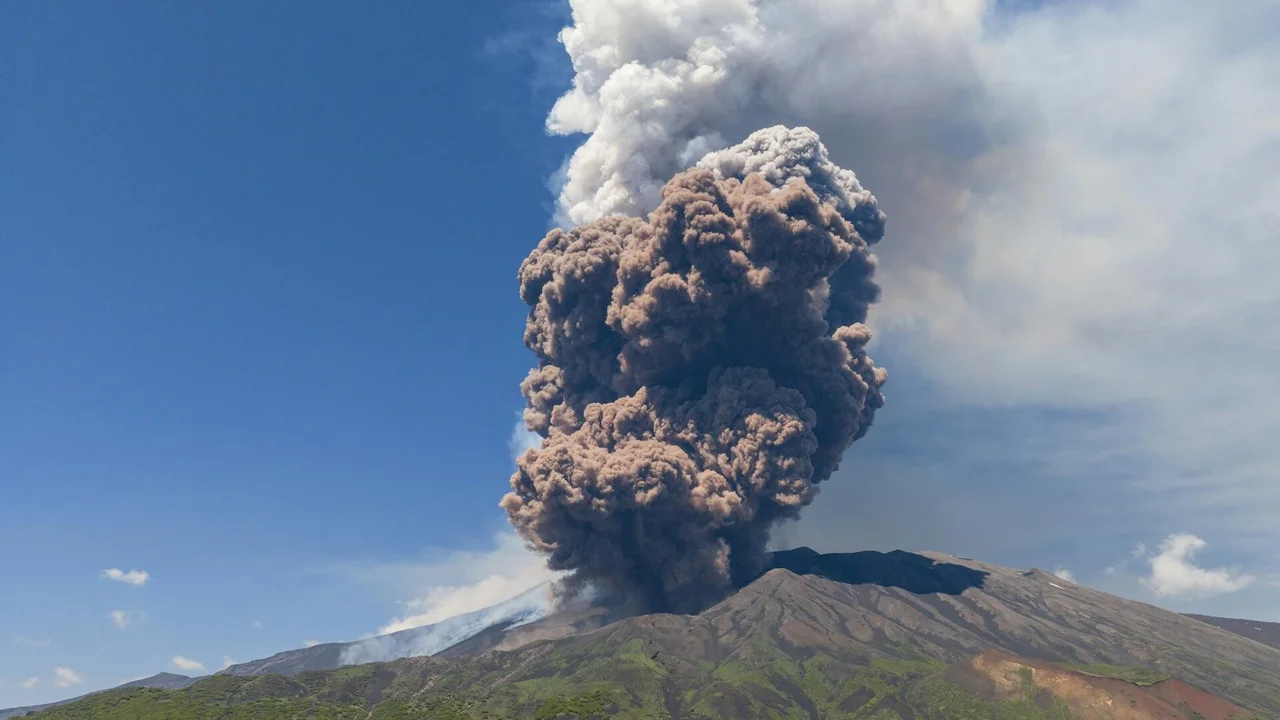
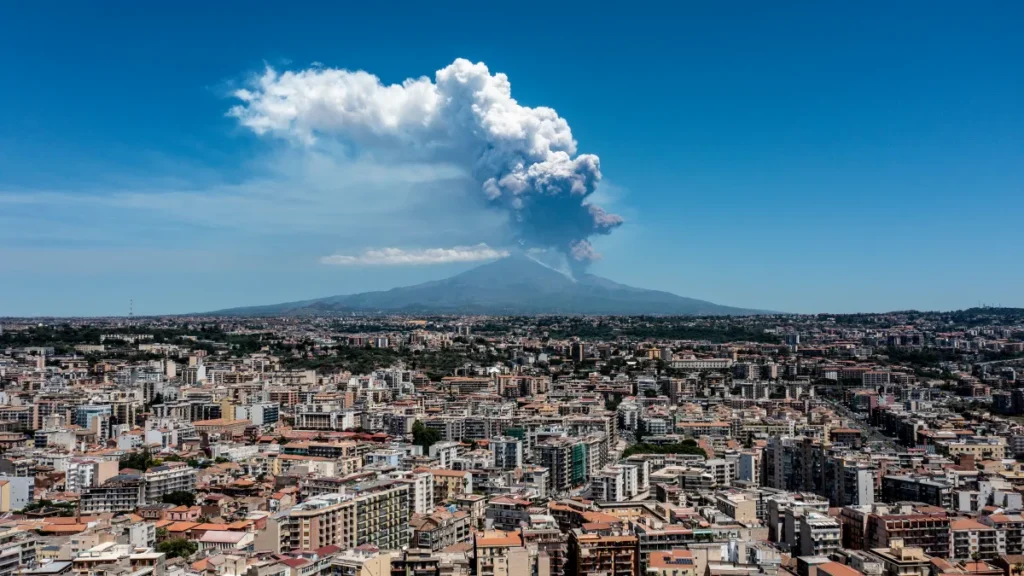
Mount Etna, Europe’s most active volcano, erupted spectacularly on Monday, sending plumes of hot ash and rivers of molten lava cascading down its slopes in a dramatic display of nature’s power.
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology’s Etna Observatory in Catania estimated the volcanic cloud’s height at about 21,325 feet. The massive ash cloud was moving in a west-southwest direction.

Volcano:

• A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust through which molten rock (magma), gases, and ash escape.
• Volcanoes form due to tectonic activity, where magma rises through cracks in the Earth’s surface.
• The movement of tectonic plates plays a crucial role in volcanic eruptions.
About Mount Etna Volcano:
• Mount Etna is situated on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina and Catania.
• It is an active stratovolcano (also known as a composite volcano). This means it has a conical shape built up by many layers of hardened lava, ash, tephra, and pumice.
• Etna is located above the convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Its activity is primarily driven by the subduction of the African Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate.
Types of Volcanoes by Activity:
- Active Volcanoes – Currently erupting or showing signs of future eruptions. Example: Mount Etna (Italy).
- Dormant Volcanoes – Not erupted recently but may erupt in the future. Example: Mount Kilimanjaro (Tanzania).
- Extinct Volcanoes – No recorded eruptions and unlikely to erupt again. Example: Ben Nevis (Scotland).
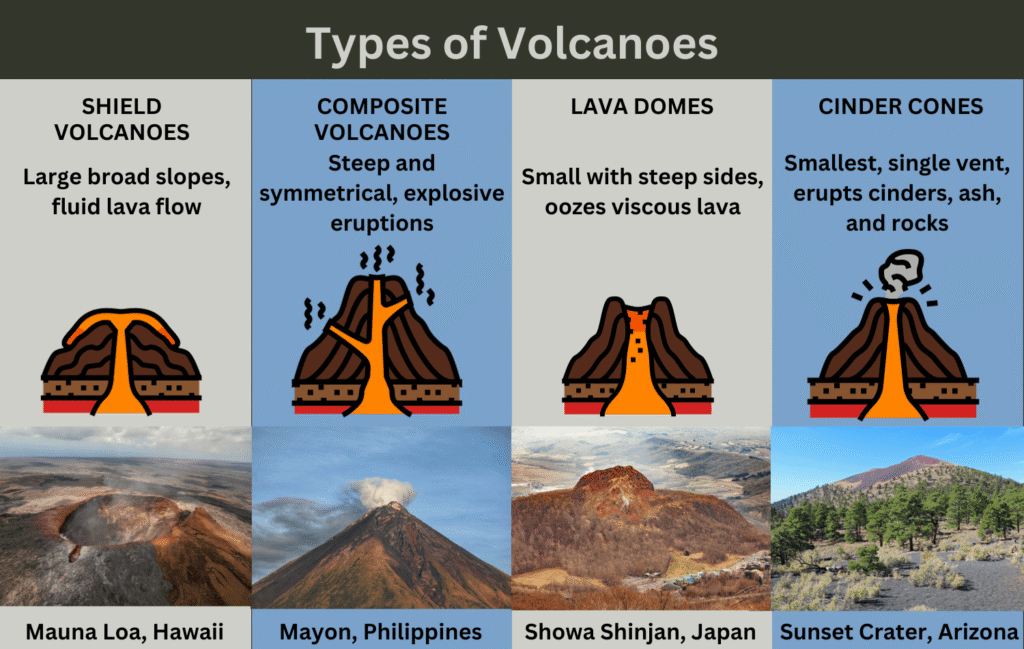
Types of Volcanoes by Shape:
- Shield Volcanoes – Broad, gently sloping volcanoes formed by fluid basaltic lava. Example: Mauna Loa (Hawaii).
- Stratovolcanoes (Composite Volcanoes) – Tall, steep-sided volcanoes built from alternating layers of lava and ash. Example: Mount Fuji (Japan).
- Cinder Cone Volcanoes – Small, steep, conical volcanoes formed by explosive eruptions of basaltic lava. Example: Paricutin (Mexico).
- Lava Domes – Dome-shaped formations created by slow extrusion of viscous lava. Example: Novarupta (USA).
- Caldera Volcanoes – Large depressions formed when a volcano collapses after a massive eruption. Example: Yellowstone Caldera (USA).
Effects of Volcanoes
• Positive Effects:
- Creates fertile soil rich in minerals.
- Forms new landmasses (e.g., Hawaiian Islands).
- Generates geothermal energy.
- Negative Effects:
- Causes destruction through lava flows and ash clouds.
- Leads to climate changes due to ash blocking sunlight.
- Triggers earthquakes and tsunamis.

