• India could become technologically capable of satellite-based quantum communication within the next 5 years, says Professor Bhaskar Kanseri of IIT-Delhi. • His team recently achieved quantum key distribution (QKD) over 1 km without using cables — the farthest such attempt in India.
What is Quantum?
Whether you know it or not, quantum physics touches our lives each day. Everything physical around us is made of matter, from the air we breathe to the water we drink—even our own bodies are made of matter. In its smallest measurable form, matter is made up of atoms. Within atoms are even smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons—and protons and neutrons are made of even smaller units of matter called quarks.
Quantum physics is the study of these extremely small atomic particles and quarks. Quantum aims to understand the nature of energy and matter through these small particles in order to better understand the world around us and apply quantum theories to real-world technology solutions.
Applied quantum science is a foundational part of many components in many modern technologies, including cell phones and computers. In quantum computing, predictions are given in terms of probability, which allows us to find answers that traditional computers cannot provide.
What is Quantum Communication?
• It enables two parties to share “quantum keys” — secure codes made from photons (light particles). • Based on quantum mechanics, particularly quantum entanglement, where changes in one photon affect its pair instantly. • Any hacking attempt becomes immediately detectable, making it extremely secure.
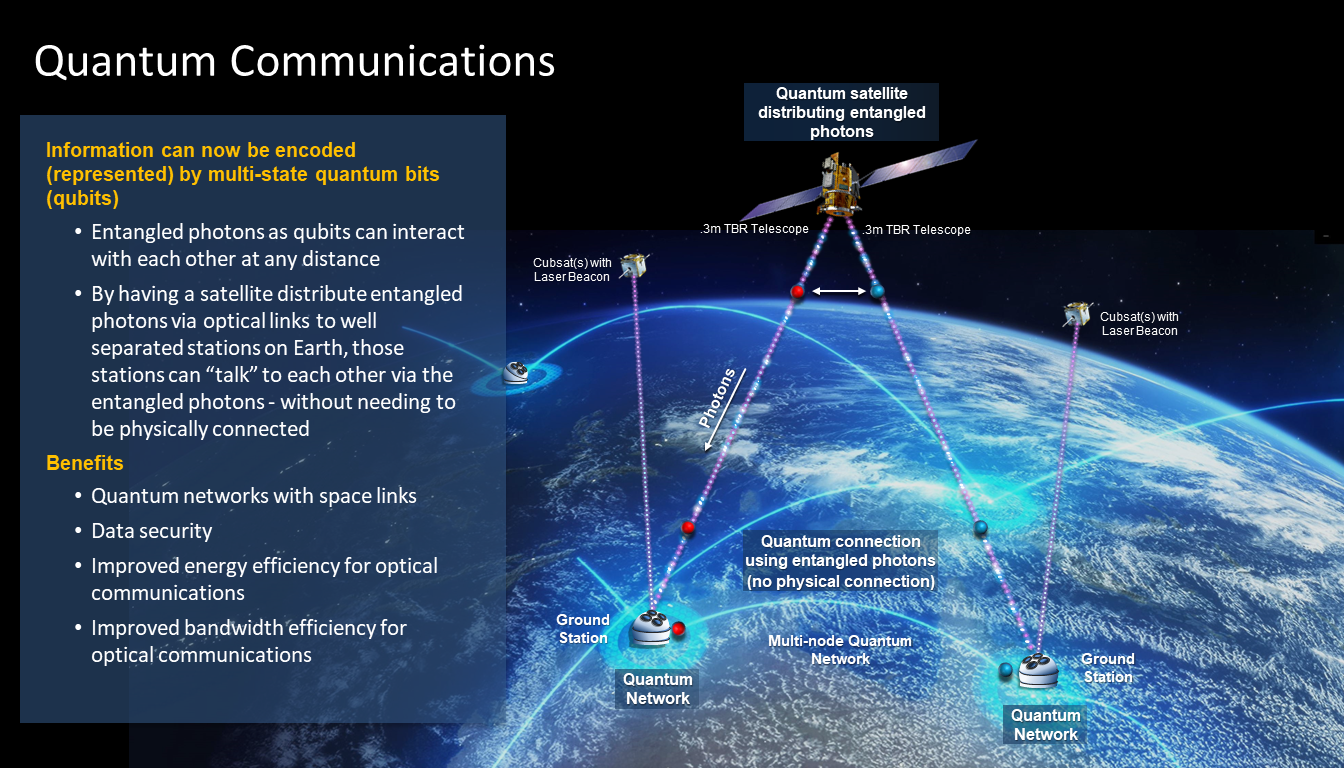
Free-Space vs Cable Transmission
• QKD can be done through fibre optic cables or through “free-space” (without cables). • Cable-based QKD is stable but becomes expensive and less feasible over long distances. • Free-space QKD using satellites is ideal for long-distance communication.
Challenges in Free-Space QKD
• Atmospheric disturbances (pollution, turbulence, airflow) affect photon transmission, especially in urban areas like Delhi. • These lead to higher error rates compared to cable-based systems. • Better beam control and signal optimisation can help reduce errors.
Global Comparison
• China successfully demonstrated satellite-based QKD nearly 10 years ago due to early investment in the 2000s. • In 2017 and 2020, Chinese researchers exchanged quantum keys between satellites and ground stations 1,000–1,700 km apart.
India’s Current Status
• IIT-Delhi’s experiments are at proof-of-concept stage with a small team of 4–5 students.
• Moving forward will require well-funded, multidisciplinary teams and active start-up involvement.
-
04/02/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 04-02-2026 Mains iMpact 04-02-2026
-
03/02/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 03-02-2026 Mains iMpact 03-02-2026
-
02/02/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 02-02-2026 Mains iMpact 02-02-2026
-
01/02/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 01-02-2026 Mains iMpact 01-02-2026
-
31/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 30-01-2026 Mains iMpact 30-01-2026
-
30/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 30-01-2026 Mains iMpact 30-01-2026
-
January 2026 Monthly Current Affairs Prelims Edge

-
January 2026 Monthly Current Affairs Mains Compilation

-
29/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 29-01-2026 Mains iMpact 29-01-2026
-
28/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 28-01-2026 Mains iMpact 28-01-2026
-
27/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 27-01-2026 Mains iMpact 27-01-2026
-
26/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 26-01-2026 Mains iMpact 26-01-2026
-
25/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 25-01-2026 Mains iMpact 25-01-2026
-
24/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 24-01-2026 Mains iMpact 24-01-2026
-
23/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 23-01-2026 Mains iMpact 23-01-2026
-
22/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 22-01-2026 Mains iMpact 22-01-2026
-
21/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 21-01-2026 Mains iMpact 21-01-2026
-
20/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 20-01-2026 Mains iMpact 20-01-2026
-
18/01/2026 || Prelims Edge & Mains iMpact

Prelims Edge 18-01-2026 Mains iMpact 18-01-2026

